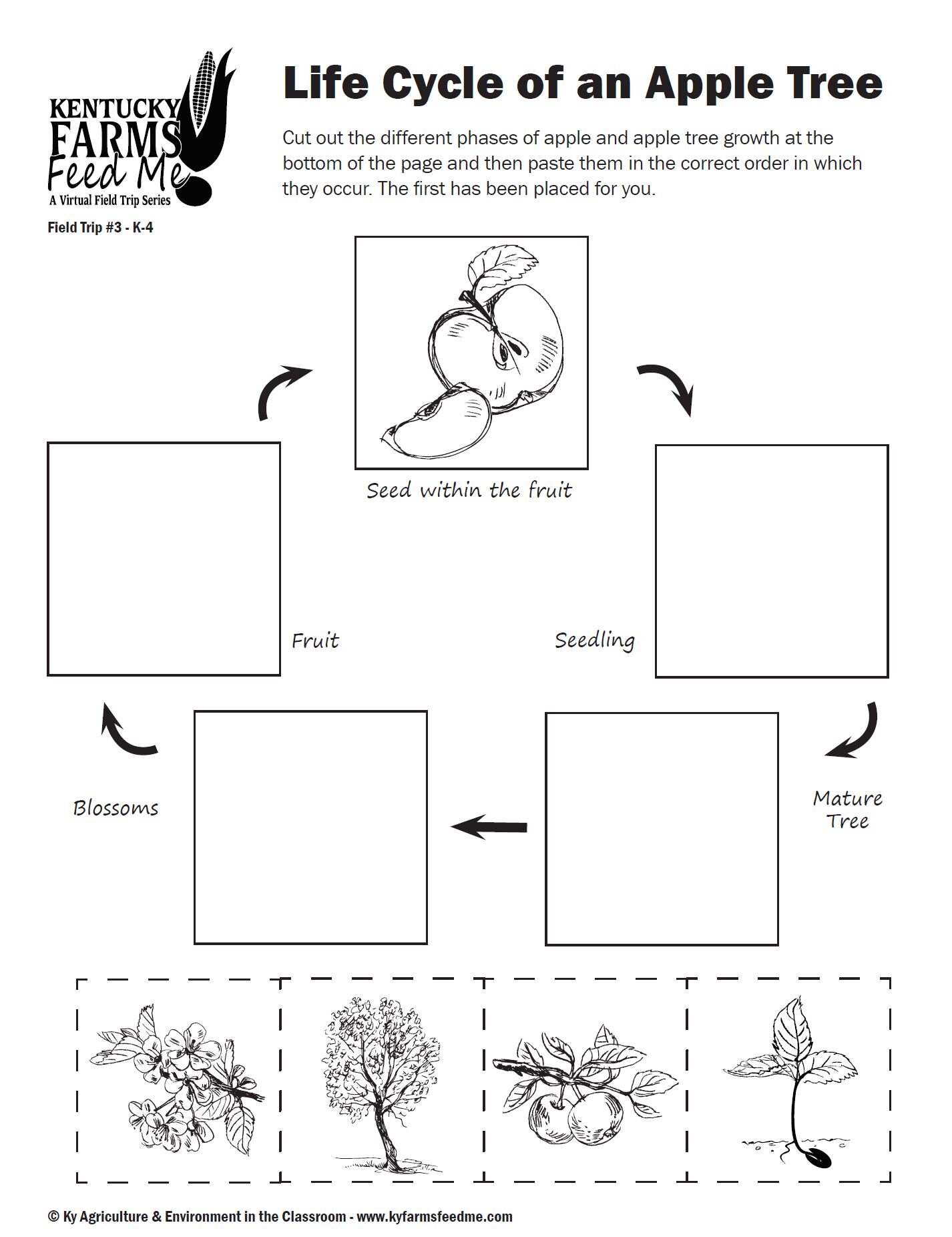
Life Cycle of an Apple Tree
Grade Level(s): Grades 2 & 3
Estimated Time: 60 minutes
Purpose
Students will construct a diagram of an apple tree’s life cycle.
3-LS1-1. Reproduction is essential to the continued existence of every kind of organism. Plants and animals have unique and diverse life cycles.Students will develop a simple model that mimics the function of bees in pollinating apple blossoms.
2-LS2-2. Develop a simple model that mimics the function of an animal in dispersing seeds or pollinating plants.3-LS2-1. Construct an argument that some animals form groups that help members survive.
Materials
Optional Materials
BOOK - How Do Apples Grow? by Betsy Maestro or How Do Apples Grow? by Jill McDonald
Parts of a Flower Google Slide (4th Grade)
Parts of a Honey Bee Google Slide (4th Grade)
Background Information
Source: http://www.usapple.org.
In winter, the apple tree rests. On the branches are buds, some of which contain leaves and others that contain five flowers. With warmer spring weather, the leaf buds unfold and flower buds begin to grow on the ends of the twigs.
Honeybees are attracted to apple flowers by nectar and the scent of the petals. As the bee collects nectar, it also picks up pollen. When the bee lands on a flower on another tree, it brushes against the pistil of the flower, leaving pollen grains on the sticky stigma. The pollen grains send tubes down through the styles to reach the ovary (pollination). Through the filament, the stamen’s pollen can reach the ovules that are in the ovary. The fertilized ovules will become seeds. More on apple pollination.
The outer wall of the ovary develops into the fleshy white part of the apple. The inner wall of the ovary becomes the apple core around the seeds.
In summer, the apples grow bigger and gradually change color, and the tree produces new growth. In fall, the apples ripen. About two weeks before the harvest, the apples’ food supply from the tree is cut off and the apples become sweeter. Most apples are harvested by hand, primarily in September and October.
Source: Ky Ag & Environment in the Classroom - Even though apple trees can be grown from a seed, most farmers use grafted saplings, or young trees, they receive from a nursery. Farmers do this to control the apple variety and size of the tree. If you plant an apple seed, you need to plant more than one (apple trees are not self-pollinating: the Golden Delicious is an exception).
The tree will also grow very large, and it may take 5 to 8 years before it produces any fruit. A grafted, dwarf tree will produce fruit much sooner, at about 3 years.
Google Slide Versions - Be sure to copy the file to your Drive or Classroom so you may assign or share with your students.