Secondary Lessons & Resources
Students (grade 3+) learn how agriculture is brings to life all of their holiday favorites! From Christmas trees to sweet treats, this interactive resource demonstrates that without farmers, it would be a blue Christmas.
MATH: There are four versions of this worksheet: Counting/Number ID, Simple Addition and Subtraction to 6, Multiplication, and Fraction Conversion.
This fun activity helps students learn who is responsible for getting bacon from the farm to the store. It also teaches interdependence.
Secondary Careers & Social Studies: Define consumer products and know the importance of agriculture and agriculture products in a healthy community. This lesson also includes an activity that shows the power of shopping locally.
Intermediate Science: Students will learn the different parts of the farm ecosystem and discuss what happens when one or more parts are missing.
Intermediate Science: Students will model the food chain from the sun to decomposers using producer and consumer examples that are found on a farm.
Intermediate & Secondary Economics: Students will understand that the foods and natural resources they consume come from a broad ecosystem due to our farming, transportation, and commerce systems.
Where does our food and clothing come from? There’s a lot more to Agriculture, the system that provides us with crops we eat and fibers we use to make clothing, than most people are aware of. Students will learn about this amazing modern industry with roots that stretch back to the beginning of civilization through the Modules and Units that cover a wide range of topics. Everyone is sure to learn something new!
Students will explore concepts of heredity in beef cattle and identify dominant and recessive traits.
Grades 4+: This Google Slide presentation focuses on how Kentucky farmers control soil erosion, as soil is one of our most precious resources for food production. The last slide provides a video demo of how different soil coverings impact how much soil washes away during a rain storm.
This 60-minute documentary features innovative farmers and soil health experts from throughout the U.S. Accompanying lesson plans for college and high school students. It starts with a reminder of the Dust Bowl and how today’s farmers are improving soil health.
Grades 4+: Students will develop an appreciation and understanding of the natural development of seeds, learn the anatomy and function of each seed part through a seed dissection, and classify seeds as monocots or dicots.
This map shows the farm and forest resources from each county and it may be used to explain regional differences and the economic factors that impact production and where processors may be located.
The following is a great companion to the Kentucky Farms Feed Me Virtual Field Trip to a Pig Farm for secondary agriculture students.
Secondary Agriculture, Foods: Our mission is to prepare students for a specialized job in poultry husbandry and processing upon graduation.
View profiles of people who work in Kentucky agriculture, or trained in Kentucky for their career.
This fun activity helps students learn who is responsible for getting milk from the cow to the glass. It also teaches interdependence.
In this lesson, students will follow the farm to fork process of producing beef, learn how cattle and other ruminants convert grass into nutrient-rich foods such as milk and meat, discover ways cattle recycle food waste, and identify careers in the beef cattle industry.
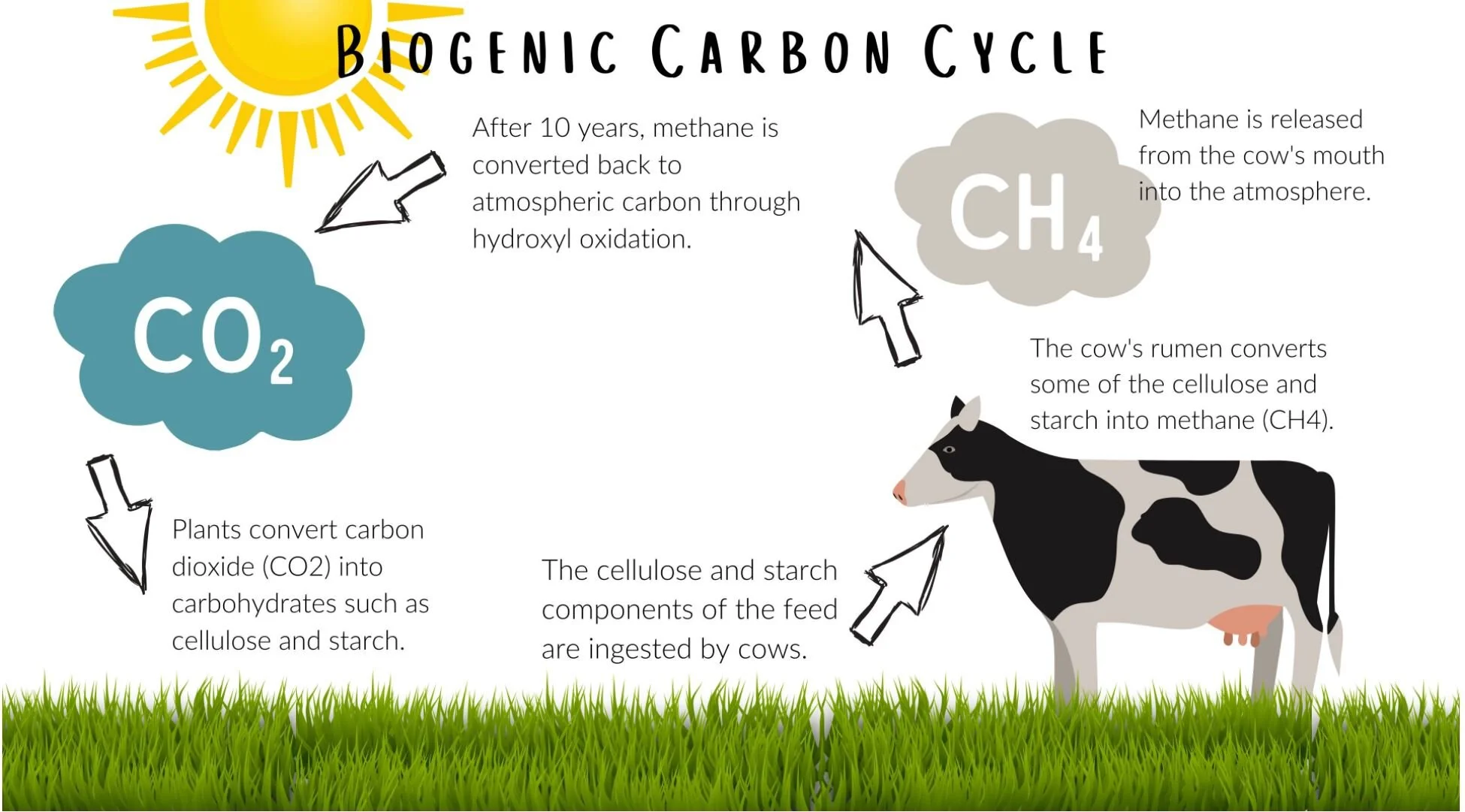
Students will explore the carbon cycle and evaluate the carbon footprint of cattle. Using critical thinking skills, students will use the Claim, Evidence, and Reasoning model to determine the effect of cows’ methane production on the environment and investigate the extent cattle contribute to climate change.
Students will compare the components of beef and plant-based burgers by determining the production and processing methods of each product; evaluate the ingredients and nutritional differences between beef and plant-based products; and discuss different points of view in the agricultural industry concerning plant-based proteins and traditional beef.
Students will evaluate the USDA grading system for whole cuts of beef and discuss consumer preferences and nutritional differences between grain-finished and grass-finished beef. Students will also distinguish various labels on beef products and discuss reasons for the government’s involvement in agricultural production, processing and distribution of food.
Ethanol is a common alcohol made by fermenting the sugar and starch components of renewable plant materials by using yeast. Humans discovered ethanol not long after they figured out how to put fire to good use.
Find lessons, fact sheets, and resources for grades K-12 on biofuels, renewable fuels, ethanol, and biodiesel.
Biodiesel is a renewable, clean-burning diesel replacement made from a diverse mix of feedstocks including recycled cooking oil, plant oils (primarily soybean oil), and animal fats.
Find several resources and activities that will help intermediate and secondary students understand the wide range of options for jobs in agriculture and food manufacturing. We have included several profiles of real professionals working in Kentucky.
Middle School Financial Literacy - Influences and Consumer Decisions
Grades: 4-5 Social Studies, MS/HS Enrichment - Students will learn how topographic, geologic, and natural resource availability affect agriculture production in the Commonwealth.
Secondary: This lesson uses a real-world scenario of designing a garden with the hopes of selling the produce it generates. Version here is developed for secondary students and could be paired with lessons on economics, plant science, meal planning, and business planning/financial literacy.